Adenoidid: Lymphoid Tissue Behind the Nasal Cavity Explained
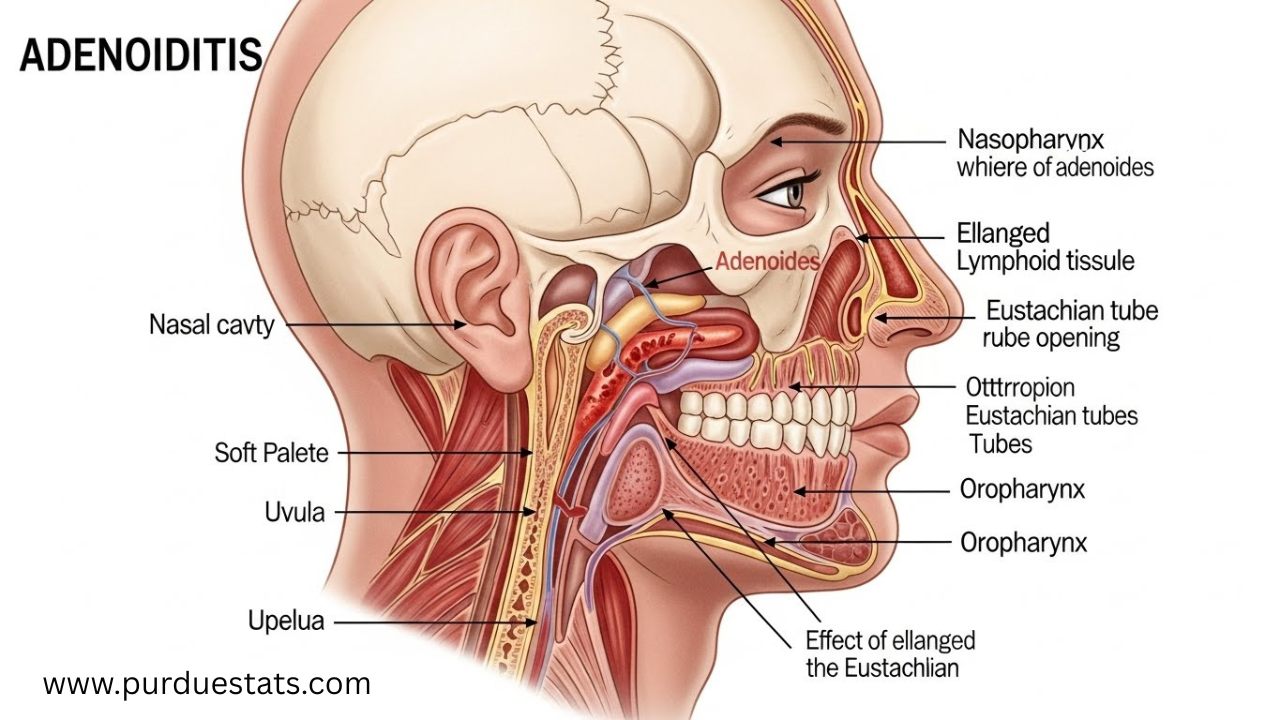
Adenoids might not be a term you hear every day, but they play an essential role in our health. Nestled at the back of the nasopharynx, these small masses of lymphoid tissue are vital players in your immune system, especially during childhood. Understanding adenoidid can help you grasp their significance and what happens when they become problematic.
Many people overlook this hidden structure until it causes issues like breathing difficulties or chronic infections. By exploring the functions, symptoms, and treatment options related to enlarged adenoids, you’ll gain valuable insights into how these tiny tissues impact overall well-being. Let’s dive deeper into the world of adenoidid and uncover what makes them so important!
Functions of Adenoids in the Body
Adenoids play a crucial role in the immune system, particularly during childhood. Located at the back of the nasopharynx, these lymphoid tissues help trap pathogens that enter through the nose and mouth.
Their primary function is to produce antibodies. These proteins are essential for fighting off infections. By recognizing harmful bacteria and viruses, adenoids aid in developing immunity.
Additionally, adenoids contribute to maintaining gut health. They work alongside other lymphatic tissues to ensure a balanced immune response throughout the body.
Interestingly, their size can change as children grow. During early years, they are relatively larger and more active in combating infections. As one transitions into adolescence and adulthood, adenoid tissue often shrinks significantly.
Thus, while they may seem small or insignificant later in life, during childhood years their functions are vital for overall health and well-being.
Common Symptoms of Enlarged Adenoids
Enlarged adenoids can lead to a variety of noticeable symptoms. One of the most common indicators is nasal obstruction. This can make breathing through the nose difficult, often resulting in mouth breathing.
Children may also experience frequent ear infections or fluid buildup in the ears. This occurs because enlarged adenoids can block the Eustachian tubes, which connect the throat to the middle ear.
Another symptom is sleep disturbances. Enlarged adenoids can contribute to snoring or even obstructive sleep apnea, disrupting restful slumber.
Additionally, persistent sore throats and bad breath may arise due to chronic inflammation. If you notice these signs in yourself or your child, it’s essential to consider a consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and care options.
Causes and Risk Factors of Adenoiditis
Adenoiditis is primarily caused by infections. Viral and bacterial pathogens often lead to inflammation of the adenoids. Common culprits include cold viruses, streptococcus bacteria, and even seasonal flu.
Children are particularly susceptible due to their developing immune systems. Frequent exposure to germs in daycare or school increases their risk of infection.
Allergies can also play a role in causing adenoid problems. When allergens trigger an immune response, they may lead to swelling and discomfort.
Environmental factors like secondhand smoke and pollution heighten the likelihood of respiratory issues that irritate the adenoids.
Genetics might contribute too; if there’s a family history of ear or throat issues, your child could be at greater risk for developing adenoiditis. Recognizing these causes helps in understanding how best to manage this condition effectively.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Adenoiditis
Diagnosing adenoiditis typically involves a thorough examination by an ear, nose, and throat specialist. The doctor will assess symptoms like nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, or recurrent ear infections. A physical exam may include looking into the throat to check for swelling.
Imaging tests such as X-rays can help visualize enlarged adenoids. In some cases, a nasopharyngoscopy might be performed using a small camera to get a closer look at the tissue.
Treatment often starts with conservative methods. This may include medications like antihistamines or nasal steroids to reduce inflammation.
If symptoms persist or worsen, surgical removal of the adenoids—called adenoidectomy—might be recommended. This procedure is generally safe and can lead to significant relief from chronic issues related to enlarged adenoids. Post-operative recovery usually involves minimal downtime for children.
Prevention of Adenoid Problems
Preventing adenoid problems begins with maintaining good overall health. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support the immune system. Fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are essential.
Regular handwashing is crucial to minimize infections. This simple practice helps reduce the spread of viruses and bacteria that could lead to adenoiditis.
Avoiding allergens also plays a significant role. Common triggers like smoke, dust, and pet dander can cause inflammation in the nasal passages. Keeping living spaces clean may alleviate some symptoms.
Encouraging children to stay hydrated is another preventive measure. Water aids in keeping mucus membranes moist, which can help prevent blockages or infections.
Routine check-ups with a healthcare professional are important for early detection of any issues related to adenoids. This proactive approach ensures timely intervention if needed.
Conclusion
Adenoidid play a crucial role in our immune system, especially during childhood. They help protect against infections by producing antibodies and trapping pathogens. However, when they become enlarged or inflamed, they can lead to various health issues.
If you notice symptoms such as difficulty breathing through the nose, persistent snoring, or recurrent ear infections in your child, it might be time to consult a healthcare provider. Understanding the causes and risk factors for adenoiditis will better equip parents to address potential concerns early on.
Diagnosis often involves physical examination and sometimes imaging studies. Treatment options range from watchful waiting to medications and even surgical removal if necessary. Preventive measures include maintaining good hygiene practices that reduce respiratory infections.
Navigating the complexities of adenoidid health is key to ensuring overall well-being for children. By staying informed about their functions and potential complications, families can seek timely interventions when needed.








